
Author: Casey McGuigan, Reveal and Slingshot Product Manager, Infragistics
Casey McGuigan holds a BA in mathematics and an MBA, bringing a data analytics and business perspective to Infragistics over the past decade. Casey is the Product Manager for the Reveal embedded analytics product and the Slingshot digital workplace platform. She is instrumental in Infragistics product development, market analysis and product go-to-market strategy.
Effective data visualization and storytelling have become crucial for organizations to make informed business decisions in today’s data-driven world. One of the most powerful tools for communicating data insights is a well-designed dashboard.
Dashboards enable business leaders and professionals to identify trends, gain actionable insights, and make data-driven decisions.
In this article, we will look at key principles and best practices for business leaders/professionals to design compelling and effective dashboards.
First, define the purpose of the dashboard. When creating a dashboard, start by clarifying the specific goals and objectives you want to achieve. Are you designing the dashboard to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), track progress toward goals, or identify trends and patterns?
Here are four dashboard categories to help you characterize the purpose of yours:
Who will view and use the dashboard for decision-making? What is their level of familiarity with data? Make sure to tailor the design and complexity of the dashboard to match your audience’s needs and analytical skills.
It’s easy to display all your data on the dashboard, but that may not be an effective way of telling your story. Include only the metrics that align with your dashboard’s purpose and objectives. Avoid cluttering the dashboard with unnecessary information and insights.
Bar charts, line graphs, and pie charts are commonly used data visualizations, but you need to make sure you choose the most suitable one for the data you are visualizing. For example, if you want to show a geographical representation of data, one appropriate option is a heat map visualization. A bar or column chart will work best if you want to compare two or more data values. A histogram is ideal if you want to perform a range analysis of data according to a specific frequency.

Provide context that explains your chart to your audience. Use descriptive and concise titles, annotations, and captions to guide the audience through trends, anomalies, and key insights. Additionally, sorting the dashboard’s content appropriately enhances its usability and helps convey the intended message effectively. For example, if your dashboard includes categories on the x-axis, sorting the data alphabetically can be beneficial, while sorting the data in ascending order is recommended when the objective is to highlight and emphasize the story of growth or progression.
Allow users to explore data on a deeper level and uncover hidden insights by incorporating different dashboard interactive elements such as dashboard linking and drill down. Dashboard linking capability connects different dashboards or visualizations together to provide a more comprehensive and detailed view of the data. The drill-down capability allows users to navigate from a high-level summary or overview dashboard to more detailed levels of information.
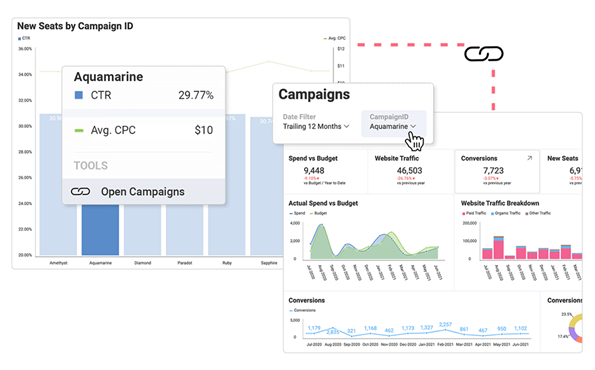
Regularly seek feedback and refine your dashboards to make them more informative, more effective, and up to date. Ensure data credibility and accuracy, update your charts and graphs when necessary, and refine the dashboard design based on your audience feedback to optimize usability and effectiveness.
Telling data stories through effective dashboard design is an essential skill for business leaders and professionals seeking to leverage their organization’s data for decision-making. By clearly defining the purpose of your dashboard and your target audience and by selecting the right metrics to visualize, business leaders/professionals can create dashboards that effectively communicate data insights and drive intelligent actions. Don’t forget to provide a narrative to your data story, enable interactive capabilities, and continuously learn the newest UI and UX trends to improve your dashboard design.